The NBIMS-US™ v4 is a consensus-based national-level standard focused on defining standard approaches and guidelines to defining requirements, planning BIM adoption, and exchanging information between project team members. MORE
The workgroup identified the most broadly adopted BIM Uses. Other BIM Uses exist outside of those identified and may be included in a future version of this module as their maturity merits inclusion. The BIM Use names are organized using verb noun format to highlight the objective being achieved by implementing the BIM Use. When referencing a BIM Use, the name of the BIM Use along with BIM Use Version should be included, i.e., Author Design (AuthorDesign- 4.0-1).
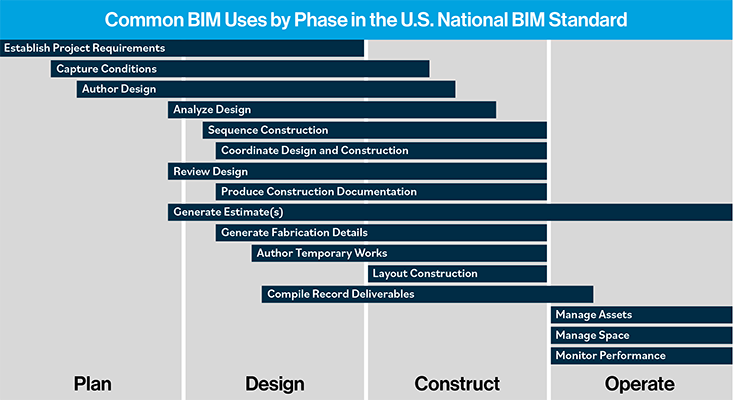
Table 1. Identified BIM Use by Typical Project Phase (Note that phases are representative only and specific BIM Use Cases can be often implemented in any phase.)
| NAME | DEFINATION | RELATED TERMS |
|---|---|---|
| GATHER | ||
| 1 Capture Conditions | Collect current information about the built environment to include in a model | Existing Condition Modeling, Laser Scanning, Reality Capture, Integrated Surveying, Photogrammetry, Photo/Video Documentation |
| GENERATE | ||
| 2 Establish Project Requirements | Capture and monitor key project aspects and scope such as area, spatial, functional, asset, deliverable, code, end user, organizational, and other stakeholder requirements using a data-centric approach. | Scoping Requirements, Identify Project Characteristics, Programming Requirements, Design Criteria, Architectural Programming |
| 3 Author Design | Develop a design using BIM authoring software with 3D and attribute information for a built environment asset leveraging an object library of parametric elements. | Design Authoring, Design Authoring and Briefing, Modeling, Discipline Modeling, Model Generation, Generative/Parametric Modeling, Federated Design Model, Design to Maintain, Product Selection, Product Library |
| 4 Generate Fabrication Details | Author manufacturing and/or construction details in a model necessary to fabricate elements of a project. | Shop Modeling, Fabrication Modeling, Construction Model, Federated Construction Model, Digital Fabrication |
| 5 Author Temporary Work | Generate the design of non-permanent elements necessary to construct a project. | Temporary Works Models, Construction System Design |
| 6 Generate Estimates | Extract project, site, and asset quantity information from model(s) to support the development of project and/or lifecycle cost estimates. | 5D, Quantity Takeoff, QTO, Cost Estimating, Engineers Estimate, Cost Analysis, Total Cost of Ownership |
| ANALYZE | ||
| 7 Analyze Design | Examine and evaluate a built environment asset design to assess its functionality, and compliance with various criteria and requirements. | Design Analysis, Engineering Analysis, Mechanical Analysis, Electrical Analysis, Structural Analysis, Energy Analysis, Lighting Analysis, Building System Analysis, Sustainability Analysis, Carbon Impact Analysis, emergency evacuation planning, Disaster Planning/EM Preparation, Site Analysis, Simulation, Spatial Analysis, Sustainability LEED Planning, Code Validation, Way Finding |
| 8 Sequence Construction | Represent and communicate the timing and/or sequencing of construction activities graphically using a model. | 4D Modeling, Phase Planning (4D), Constructability, Schedule Visualization, Sequencing, Site Utilization Planning, Construction Simulation, Construction Logistics, 4D Scheduling, 4D BIM |
| 9 Coordinate Design and Construction | Verify the design layout and spatial arrangement of systems by applying construction means and methods and additional spatial constraints (such as code requirements, maintenance access and clearances) to validate the constructability of the project | 3D Coordination, MEP Coordination, Clash Management, Interference management, Spatial coordination, Clash detection |
| 10 Review Design | Validate the design intent and constructability of the project based on meeting project requirements and stakeholder expectations, and regulatory compliance (such as validating design quality, 3D model quality, and data quality). | Virtual Mock-up, Data validation, Validating Project Requirements, Design Review, Model Quality Review, Value Analysis / Engineering, Constructability, Sustainability, Maintainability |
| COMMUNICATE | ||
| 11 Produce Construction Documentation | Generate documentation to communicate design intent and construction details which may include plans, elevations, sections, renderings, data schedules, 3D diagrams, or specifications. | Plans, Specifications, and Estimates (PS&E), Produce Drawings, Working Drawings, Contract Documents, Contract Drawings, CDs, Produce Documentation to Perform Procurement |
| 12 Compile Record Deliverables | Capture and document project and asset information for the purpose of communicating the work performed, progress made, and compliance with requirements at the project completion. | Record Modeling, As-Built Modeling, As-Built Markup, Turnover Documents, Digital Markups, Project Record, Facility Data/COBie Deliverable, Operations & Maintenance Manuals |
| REALIZE | ||
| 13 Layout Construction | Establish and mark features of work on a construction project using real-time positioning supported by model data. | Digital Layout, Automated Machine Guidance, Digital Control, Machine Control |
| MANAGE | ||
| 14 Manage Assets | Track asset performance and ensure proper maintenance to improve longevity and optimize functionality. | Asset Management, Asset Planning, Capital Management, Maintenance Management |
| 15 Manage Space | Allocate, organize, and optimize the use of the physical space of a built environment asset. | Space Management, Space Utilization, Space Requirement Analysis, Space Inventory, Space Allocation, Traffic Flow and Circulation Planning |
| 16 Monitor Performance | Assess and evaluate the performance of a built environment asset to ensure it operates efficiently, effectively, and with performance standards. | Monitor System Performance, Performance tracking, Building System Analysis. |
The NBIMS-US™ v4 is a consensus-based national-level standard focused on defining standard approaches and guidelines to defining requirements, planning BIM adoption, and exchanging information between project team members. MORE